Can I use the patch if the repair is incomplete?
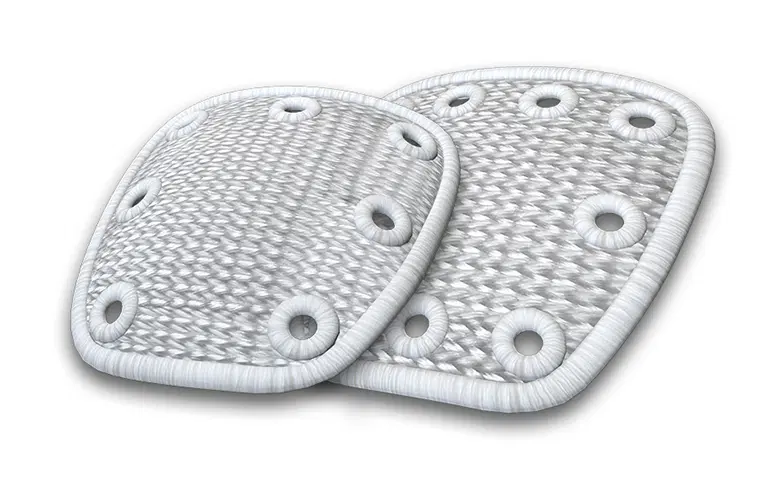
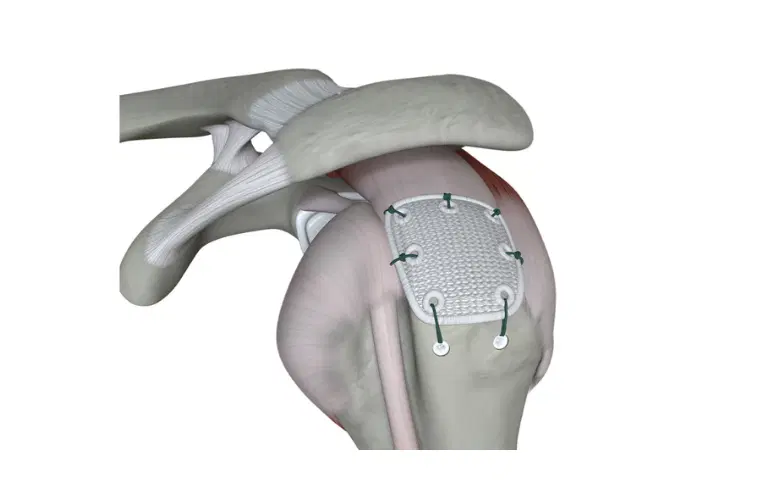
Yes, Pitch-Patch is indicated in repairs that cannot be completely repaired using standard methods, as long as it is augmenting the repair and not bridging. The strength of the device is measured when attached to sutures and the minimum strength (355N) is suitable for reinforcing the repair of torn tendon.
Can I use the patch to bridge a gap if I cannot close the repair
No, Pitch-Patch is not indicated for bridging or interposition. It is for augmentation.
Can I switch from arthroscopic approach to open approach during a procedure and then use the patch?
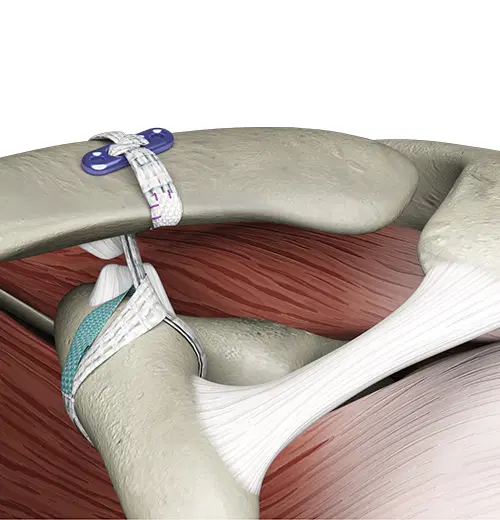
Yes, the Pitch-Patch can be used with open or arthroscopic method. Arthroscopic method uses a “parachute” technique to place the device. A decision to change to open approach should ideally be made before the parachute sutures are set up.
Are there any special rehabilitation requirements?
There are no special requirements. The patient can follow the same rehabilitation programme as for a primary rotator cuff repair.
What happens to the Pitch-Patch over time?
Pitch-Patch is gradually encapsulated after a minimal acute inflammatory reaction. Unlike certain biological implants, the polyester material does not cause any immunological reaction. It then integrates well with the patient’s tissues. It is not absorbed, no is any significant change in tensile strength known to occur in vivo.
Pitch-Patch is permanent, can it be removed?
Pitch—Patch has been shown to integrate well with the patient’s tissue. Tissue incorporates between and around the polyester fibres. In the study by Smolen et al seven revisions were successfully carried out, removing the implant where required. It may not be a suitable option where eventual removal of the device is planned or anticipated.
Does a permanent implant lead to crepitus or frozen shoulder?
Published clinical data reports the levels of complications including frozen shoulder, arthrofibrosis and crepitus. Xiros also collect post-market data. The levels of all such complications recorded to date are within the expected levels for rotator cuff repair with or without patch augmentation.